support@comsol.com
Microfluidics Module Updates
For users of the Microfluidics Module, COMSOL Multiphysics® version 6.2 introduces a Free and Porous Media Flow, Darcy multiphysics coupling for modeling flow in connected porous and nonporous domains, as well as an Incompressible Potential Flow interface for initializing laminar flow models or performing fast simulations of flow in Hele-Shaw cells. Learn more about these updates below.
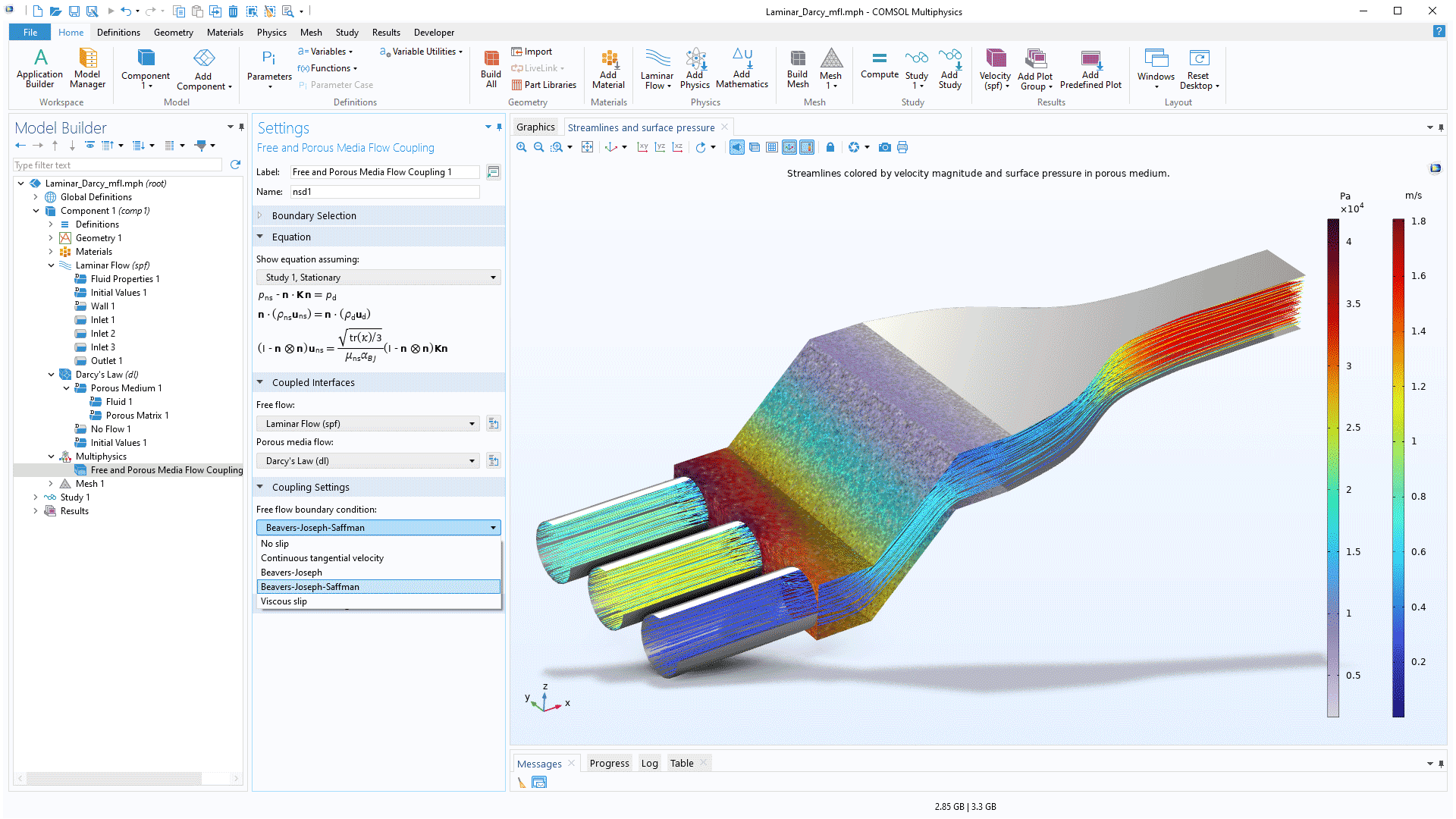
Flow in Connected Porous and Nonporous Domains
A new multiphysics interface for free and porous media flow enables laminar flows in nonporous domains to be connected with flows in porous domains modeled by Darcy's law. This functionality enables the modeling of flows in applications including biological tissue, microscale filtration, electrochemical cells, and seepage. The free flow boundary conditions, No slip, Continuous tangential velocity, Beavers-Joseph, Beavers-Joseph-Saffman, and Viscous slip, can be applied at the interface between the nonporous and porous domains. Note that the previously available Free and Porous Media Flow interface has been renamed to Free and Porous Media Flow, Brinkman.
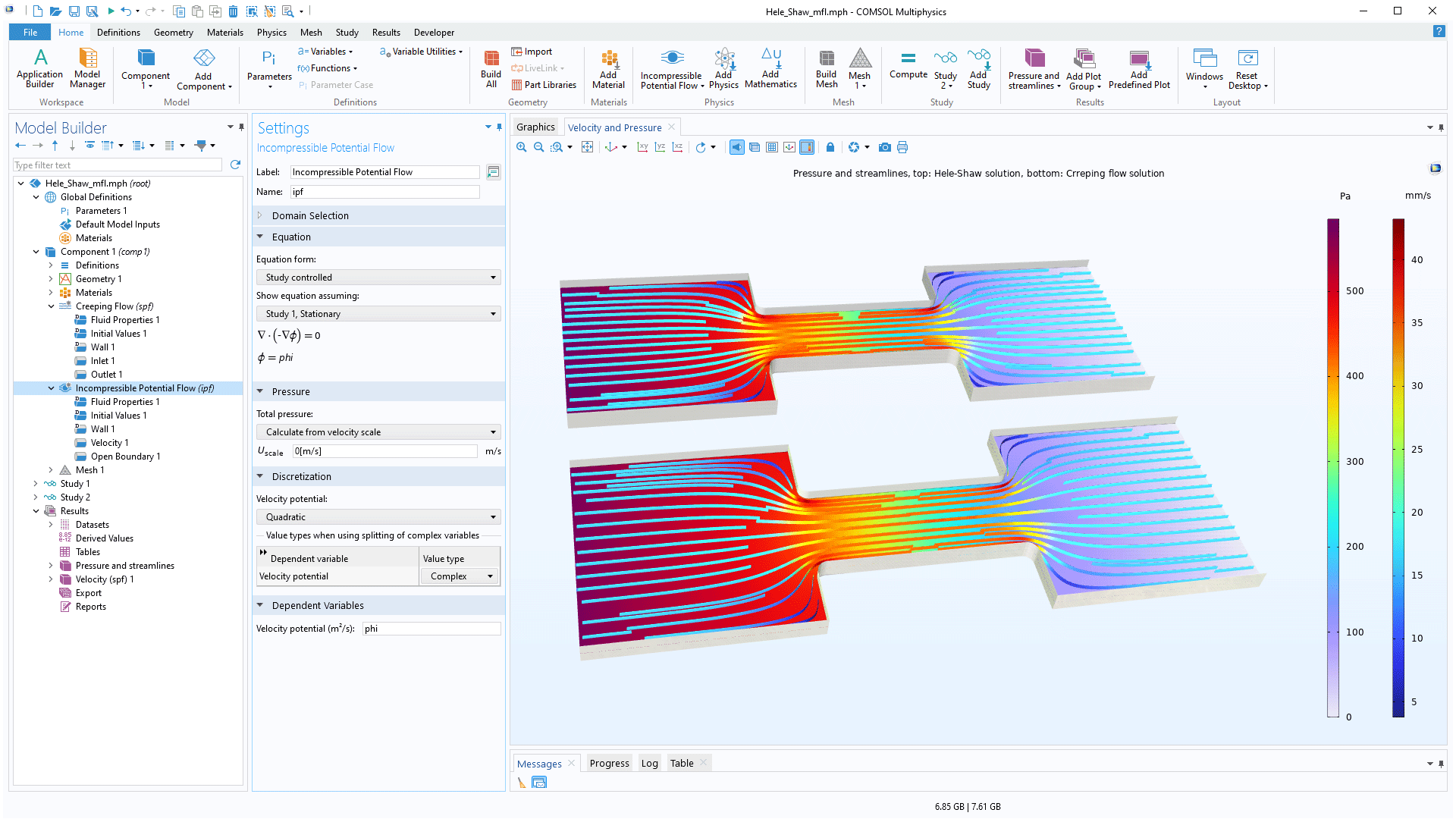
Flow Initialization and Hele-Shaw Flow
A new Incompressible Potential Flow interface under the Potential Flow section has been added to the Fluid Flow branch. Flow that is simultaneously solenoidal and irrotational can be represented as incompressible potential flow, and, in many scenarios, this approach provides reasonably accurate approximations that solve quickly. This interface can also be used to obtain initial values for more complex fluid flow models that include rotational effects. In addition, potential flow can be used to model creeping flow between parallel plates in, for example, Hele-Shaw cells.