Resources
White Papers and Application Notes
A Comparison Between an A-V and V Formulation in Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
Published in 2013
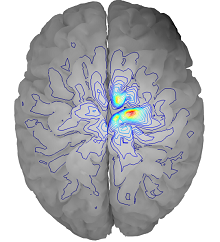
The prediction of the exact location and intensity of the electric field induced in the human brain during Transcranial magnetic stimulation is a nontrivial computational task. Numerical simulations of the procedure can be used to acquire first approximations in a safe and controlled environment. In order to make this approach more accessible, it is necessary to reduce computation time as much as possible while maintaining a satisfactory level of accuracy. The focus of this paper is to compare an A-V (magnetic vector potential, electric scalar potential) and V (electric scalar potential) formulation in terms of accuracy, memory requirements and computation time.
Download
- granula_poster.pdf - 0.93MB
- granula_paper.pdf - 1MB
- granula_abstract.pdf - 0.34MB
